Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
EXP3 Bandit cumulative regret¶
This script shows how to define a bandit environment and an EXP3 randomized algorithm.
import numpy as np
from rlberry_research.envs.bandits import AdversarialBandit
from rlberry_research.agents.bandits import (
RandomizedAgent,
TSAgent,
makeEXP3Index,
makeBetaPrior,
)
from rlberry.manager import ExperimentManager, plot_writer_data
# Agents definition
class EXP3Agent(RandomizedAgent):
name = "EXP3"
def __init__(self, env, **kwargs):
prob, tracker_params = makeEXP3Index()
RandomizedAgent.__init__(
self,
env,
prob,
writer_extra="action",
tracker_params=tracker_params,
**kwargs
)
class BernoulliTSAgent(TSAgent):
"""Thompson sampling for Bernoulli bandit"""
name = "TS"
def __init__(self, env, **kwargs):
prior, _ = makeBetaPrior()
TSAgent.__init__(self, env, prior, writer_extra="action", **kwargs)
# Parameters of the problem
T = 3000 # Horizon
M = 20 # number of MC simu
def switching_rewards(T, gap=0.1, rate=1.6):
"""Adversarially switching rewards over exponentially long phases.
Inspired by Zimmert, Julian, and Yevgeny Seldin.
"Tsallis-INF: An Optimal Algorithm for Stochastic and Adversarial Bandits."
J. Mach. Learn. Res. 22 (2021): 28-1.
"""
rewards = np.zeros((T, 2))
t = 0
exp = 1
high_rewards = True
for t in range(T):
if t > np.floor(rate**exp):
high_rewards = not high_rewards
exp += 1
if high_rewards:
rewards[t] = [1.0 - gap, 1.0]
else:
rewards[t] = [0.0, gap]
return rewards
rewards = switching_rewards(T, rate=5.0)
# Construction of the experiment
env_ctor = AdversarialBandit
env_kwargs = {"rewards": rewards}
Agents_class = [EXP3Agent, BernoulliTSAgent]
agents = [
ExperimentManager(
Agent,
(env_ctor, env_kwargs),
init_kwargs={},
fit_budget=T,
n_fit=M,
parallelization="process",
mp_context="fork",
)
for Agent in Agents_class
]
# these parameters should give parallel computing even in notebooks
# Agent training
for agent in agents:
agent.fit()
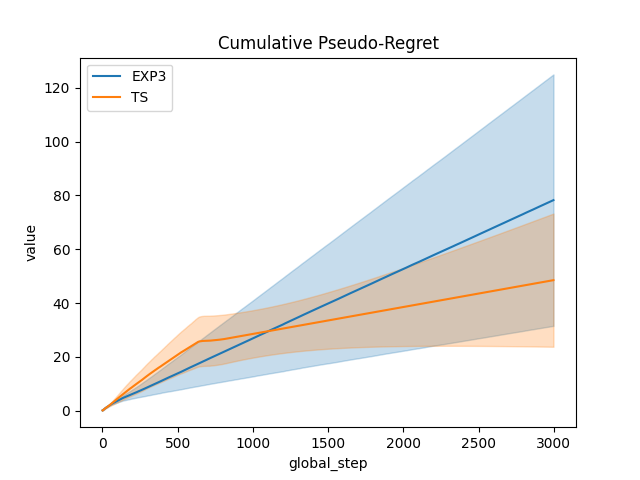
# Compute and plot (pseudo-)regret
def compute_pseudo_regret(actions):
selected_rewards = np.array(
[rewards[t, int(action)] for t, action in enumerate(actions)]
)
return np.cumsum(np.max(rewards, axis=1) - selected_rewards)
output = plot_writer_data(
agents,
tag="action",
preprocess_func=compute_pseudo_regret,
title="Cumulative Pseudo-Regret",
)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 7.308 seconds)