Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
UCB Bandit cumulative regret¶
This script shows how to define a bandit environment and an UCB Index-based algorithm.
import numpy as np
from rlberry_research.envs.bandits import NormalBandit
from rlberry_research.agents.bandits import IndexAgent, makeSubgaussianUCBIndex
from rlberry.manager import ExperimentManager, plot_writer_data
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Agents definition
class UCBAgent(IndexAgent):
"""UCB agent for sigma-subgaussian bandits"""
name = "UCB Agent"
def __init__(self, env, sigma=1, **kwargs):
index, _ = makeSubgaussianUCBIndex(sigma)
IndexAgent.__init__(self, env, index, writer_extra="action", **kwargs)
# Parameters of the problem
means = np.array([0, 0.9, 1]) # means of the arms
T = 3000 # Horizon
M = 20 # number of MC simu
# Construction of the experiment
env_ctor = NormalBandit
env_kwargs = {"means": means, "stds": 2 * np.ones(len(means))}
xp_manager = ExperimentManager(
UCBAgent,
(env_ctor, env_kwargs),
fit_budget=T,
init_kwargs={"sigma": 2},
n_fit=M,
parallelization="process",
mp_context="fork",
)
# these parameters should give parallel computing even in notebooks
# Agent training
xp_manager.fit()
# Compute and plot (pseudo-)regret
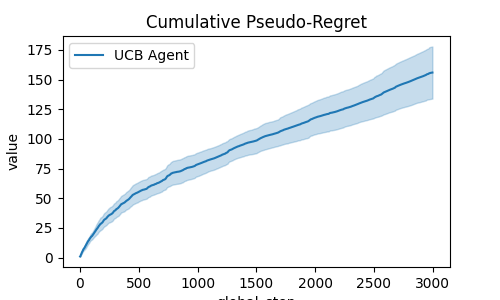
def compute_pseudo_regret(actions):
return np.cumsum(np.max(means) - means[actions.astype(int)])
fig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(5, 3))
ax = plt.gca()
output = plot_writer_data(
[xp_manager],
tag="action",
preprocess_func=compute_pseudo_regret,
title="Cumulative Pseudo-Regret",
ax=ax,
)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 4.657 seconds)